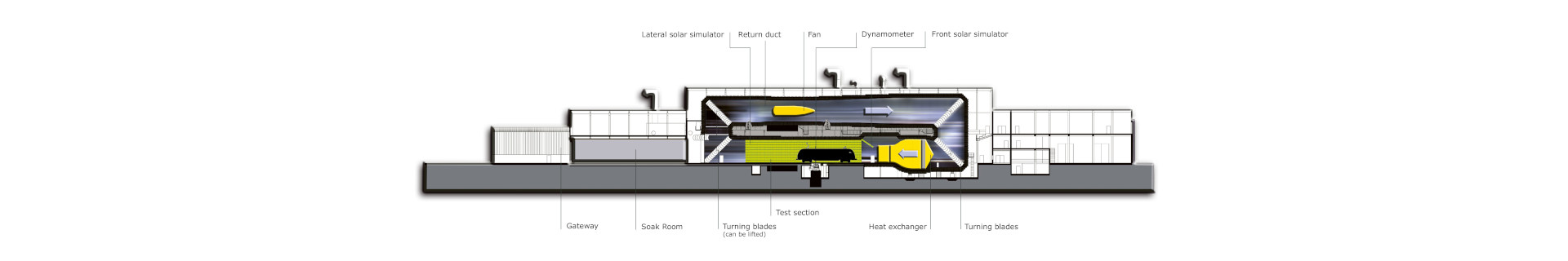
Test section length 33,8 m
Maximum temperature gradient -45°C to +60°C
Maximum wind speed 120 km/h
Relative humidity at temperatures > 10°C 10 to 98%
Solar simulation

A lateral solar panel is installed to simulate solar radiation on vehicle side wall and roof areas at a 30° angle of incidence. The panels are arranged to cover the roof and one side of the vehicle to ensure homogenous radiation input. The intensity can be continuously adjusted from 250 W/m to 1000 W/m. The solar radiation panel has a length of 30 m.
Another solar panel is installed in the flow area of each test section in order to simulate solar radiation on the front parts of a vehicle, such as the driver’s cab. The panel is arranged so as not to disturb flow characteristics and can be adapted to vehicle geometries, i.e. the angle of incidence can be varied from 0° to 90°. Again, the radiation intensity can be freely adjusted from 250 W/m to 1000 W/m.
Rain, snow and ice simulation

The simulation of snow, rain and ice plays a major role in climatic testing along with temperature, humidity and solar radiation. The climatic wind tunnels are equipped with various devices specially designed for this purpose.
A spray rig can be inserted into both climatic wind tunnels so that the entire frontal part of the vehicle can be uniformly covered with rain, snow and ice. The ultra-fine snow and ice nozzles are designed to produce droplets down to sizes of < 20 µm (see Spraytec droplet measuring instrument). This feature is especially important when carrying out tests for the aviation industry, where subcooled water droplets must be simulated.
Connections for individual nozzles are arranged along the test section to allow for local snow and ice application. The system can be used at air speeds of up to 160 km/h and temperatures down to -20 °C.
An additional rain rig for rain and ice tests is installed in the ceiling. It can be set to a precipitation rate of up to 80 l/(hm) over the entire test section (in both climatic wind tunnels simultaneously). The rig sections in the tunnels are divided into segments of 15 m each, which can be activated or shut off separately.
For certain functional tests, e.g. on high-voltage disconnecting switches or current collectors, subcooled water must be used for the production of clear ice. The facility is equipped with a water cooling system and a pump unit for this purpose.
Dynamometer, Idle City and exhaust system

The dynamometer for road vehicles installed in the central part of the test section has a drive power of 250 kW and a braking power of 300 kW.
The airflow to the front of the test object can be shut off completely by means of flaps installed at the head of the test section. This “Idle City System” is designed to simulate, e.g., a stop-and-go cycle with doors opening.
Two outlets, one located in the ceiling and one in the wall in the central part of the tunnel, are provided to discharge exhaust gases from combustion engines. If both exhaust outlets are used simultaneously, the exhaust air volume discharged can be adjusted from 0.32 to 3.2 kg/s at 200°C. If only the wall exhaust outlet is used, an exhaust air volume of up to 0.7 kg/s at 600°C is possible (in particular for road vehicles).